PC Components, Features, and System Design
A modern PC is both simple and complicated. It is simple in the sense that over the years, many of the components used to construct a system have become integrated with other components into fewer and fewer actual parts. It is complicated in the sense that each part in a modern system performs many more functions than did the same types of parts in older systems.
Here are the components and peripherals necessary to assemble a basic modern PC system:
- Motherboard
- Processor
- Memory(Ram)
- Case(Chassis)
- Power Supply
- Hard Drive
- Cd-Rom/DVD-Rom
- Video Card
- Sound Card
- Mouse
- Keyboard
- Monitor(Display)
Motherboard

The main printed circuit board in a computer is known as the motherboard. Other names for this central computer unit are system board, mainboard, or printed wired board (PWB).
The motherboard is sometimes shortened to Mobo. Numerous major components, crucial for the functioning of the computer, are attached to the motherboard. These include the processor, memory, and expansion slots. The motherboard connects directly or indirectly to every part of the PC.
The type of motherboard installed in a PC has a great effect on a computer's system speed and expansion capabilities.
Processor

A processor, or "microprocessor," is a small chip that resides in computers and other electronic devices. Its basic job is to receive input and provide the appropriate output. The central processor of a computer is also known as the CPU, or "central processing unit.
Modern CPUs often include multiple processing cores, which work together to process instructions. While these "cores" are contained in one physical unit, they are actually individual processors. In fact, if you view your computer's performance with a system monitoring utility like Windows Task Manager (Windows) or Activity Monitor (Mac OS X), you will see separate graphs for each processor.
Processors that include two cores are called dual-core processors, while those with four cores are called quad-core processors. Some high-end workstations contain multiple CPUs with multiple cores, allowing a single machine to have eight, twelve, or even more processing cores.
Memory(Ram)

RAM (pronounced ramm) is an acronym for random access memory, a type of computer memory that can be accessed randomly; that is, any byte of memory can be accessed without touching the preceding bytes. RAM is found in servers, PCs, tablets, smartphones and other devices, such as printers.
There are two main types of RAM: DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory) SRAM (Static Random Access Memory). DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory) – The term dynamic indicates that the memory must be constantly refreshed or it will lose its contents.
DRAM is typically used for the main memory in computing devices. If a PC or smartphone is advertised as having 4-GB RAM or 16-GB RAM, those numbers refer to the DRAM, or main memory, in the device.
SRAM (Static Random Access Memory) – While DRAM is typically used for main memory, today SRAM is more often used for system cache. SRAM is said to be static because it doesn't need to be refreshed, unlike dynamic RAM, which needs to be refreshed thousands of times per second. As a result, SRAM is faster than DRAM. However, both types of RAM are volatile, meaning that they lose their contents when the power is turned off.
Case/Chassis

Alternatively referred to as the computer case and sometimes referred to as the system unit or base unit. The chassis is the housing that helps protect and organize all the components that make up a desktop computer. The picture is an empty computer chassis.
Most people overlook the computer case as only a box, but it does provide the below important features:
- Structure - The case is what holds everything together in a compact and organized fashion.
- Protection - Without the case, each of the sensitive components in the computer would be vulnerable to dirt, foreign objects, kids, animals, as well as electrical interference (EMI / RFI).
- Cooling - The case helps keep the air properly flowing over all components, which keeps everything cool and running properly.
- Noise - Many computers and components have fans that generate noise. Having those components in a confined case reduces the overall noise.
- Aesthetics - Although some may disagree, most people would rather look at the case instead of all the circuit boards, wires, and all the components of a computer.
Power Supply

The desktop computer power supply changes alternating current from a wall socket of mains electricity to low-voltage direct current to operate the processor and peripheral devices. Several direct-current voltages are required, and they must be regulated with some accuracy to provide stable operation of the computer. A power supply rail or voltage rail refers to a single voltage provided by a power supply unit (PSU).
A power supply unit (or PSU) converts mains AC to low-voltage regulated DC power for the internal components of a computer. Modern personal computers universally use switched-mode power supplies. Some power supplies have a manual switch for selecting input voltage, while others automatically adapt to the mains voltage.
Most modern desktop personal computer power supplies conform to the ATX specification, which includes form factor and voltage tolerances. While an ATX power supply is connected to the mains supply, it always provides a 5 Volt standby (5VSB) voltage so that the standby functions on the computer and certain peripherals are powered. ATX power supplies are turned on and off by a signal from the motherboard. They also provide a signal to the motherboard to indicate when the DC voltages are in spec, so that the computer is able to safely power up and boot.
Hard Drive
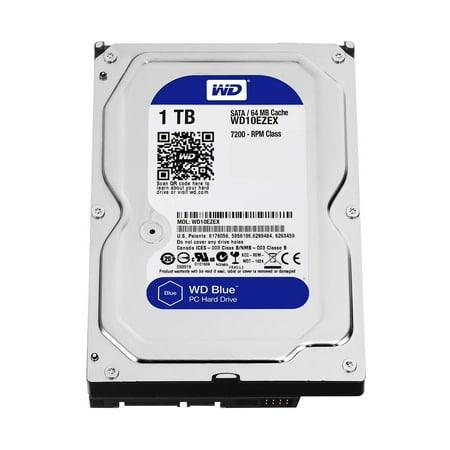

A hard disk drive (sometimes abbreviated as hard drive, HD, or HDD) is a non-volatile memory hardware device that permanently stores and retrieves data on a computer. A hard drive is a secondary storage device that consists of one or more platters to which data is written using a magnetic head, all inside of an air-sealed casing. Internal hard disks reside in a drive bay, connect to the motherboard using an ATA, SCSI, or SATA cable, and are powered by a connection to the PSU (power supply unit).
All computers have a hard drive installed in them, which is used to store files for the operating system, software programs, and a user's personal files. A computer cannot function without a hard drive installed, as it requires one to function properly.
CD-Rom/DVD-Rom

An optical drive is a piece of computer hardware about the size of a thick soft cover book. The front of the drive has a small Open/Close button that ejects and retracts the drive bay door. This is how media like CDs, DVDs, and BDs are inserted into and removed from the drive.
Most optical drives also have jumper settings on the back end that define how the motherboard is to recognize the drive when more than one is present. These settings vary from drive to drive, so check with your optical drive manufacturer for details.
Alternatively, an external optical drive may be a self-contained unit that co0nnects to a computer via a USB cable.
Video Card
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/EVGA-GeForce-GTX-1060-5886340a3df78c2ccd9f8f02.jpg)
A video card connects to the motherboard of a computer system and generates output images to display. Video cards are also referred to as graphics cards. Video cards include a processing unit, memory, a cooling mechanism and connections to a display device.
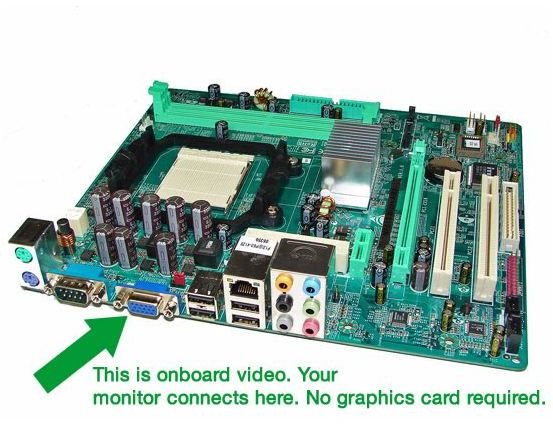
Most Motherboards have onboard video so that you do not have to buy a separate graphics card in order to have video and graphics on your PC. Desktop PCs without onboard graphics. A video card/graphics card will go into an available PCI or PCI Express slot on your motherboard.
eGPU, or external Graphics cards, is a relatively new concept that will let you turbocharge your gaming framerates for computers that cannot take an internal card. It's an external enclosure for a desktop-style video card that can plug into a laptop or other system to boost graphical performance.
Sound Card
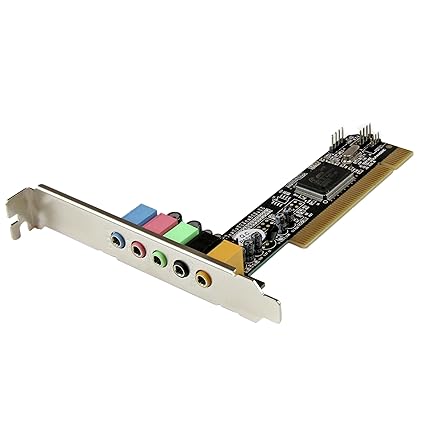


A sound card (also known as an audio card) is an internal expansion card that provides input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under control of computer programs. The term sound card is also applied to external audio interfaces used for professional audio applications.
Sound functionality can also be integrated onto the motherboard, using components similar to those found on plug-in cards. The integrated sound system is often still referred to as a sound card. Sound processing hardware is also present on modern video cards with HDMI to output sound along with the video using that connector; previously they used a S/PDIF connection to the motherboard or sound card.
Typical uses of sound cards or sound card functionality include providing the audio component for multimedia applications such as music composition, editing video or audio, presentation, education and entertainment (games) and video projection. Sound cards are also used for computer-based communication such as voice over IP and teleconferencing.
Mouse
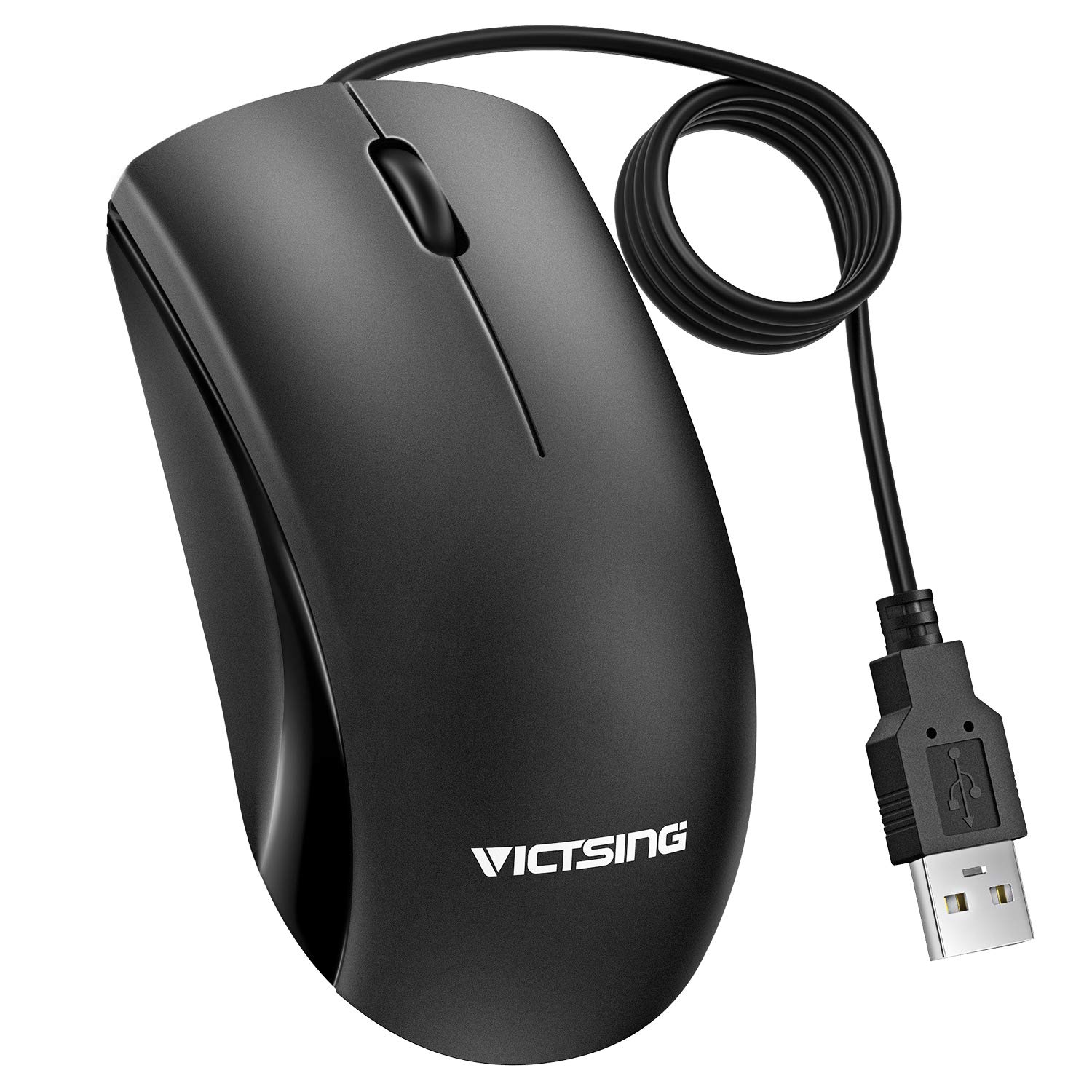

A computer mouse is an input device that is used with a computer. Moving a mouse along a flat surface can move the cursor to different items on the screen. Items can be moved or selected by pressing the mouse buttons (called clicking).[1] Today's mice have two buttons, the left button and right button, with a scroll wheel in between the two.
It is called a computer mouse because of the wire that connects the mouse to the computer. The people who designed it thought that it looked like the tail on a mouse. Today, many computer mice use wireless technology and have no wire.There are many types of mouse. Optical mouse, wireless mouse, mechanical mouse, trackball mouse. A computer mouse is a handheld hardware input device that controls a cursor in a GUI and can move and select text, icons,files,and folders. For desktop computers, the mouse is placed on a flat surface such as a mouse pad Or a desk and is placed in front of your computer. The picture to the right is an example of a desktop computer mouse with two buttons and a wheel. The mouse was originally known as the X-Y position Indicator for a display system and was invented by Douglas Engelbart in 1963 while working at Xerox PARC.However,due to Alto's lack of success, the first widely used application of the mouse was with the Apple Lisa computer.
Today this pointing device is on virtually every computer.Move the mouse cursor- The primary function is to move the mouse pointer on the screen. Open or execute a program- once you've moved the pointer to an icon, folder, or other object clicking or double clicking that object opens the document or executes the program. Pointing to an item on the screen means moving your mouse so the pointer appears to be touching the item.when you point to something, a small box often appears that describes the item.
Keyboard

A computer keyboard is an input device used to enter characters and functions into the computer system by pressing buttons, or keys. It is the primary device used to enter text. A keyboard typically contains keys for individual letters, numbers and special characters, as well as keys for specific functions. A keyboard is connected to a computer system using a cable or a wireless connection.
Most keyboards have a very similar layout. The individual keys for letters, numbers and special characters are collectively called the character keys. The layout of these keys is derived from the original layout of keys on a typewriter. The most widely used layout in the English language is called QWERTY, named after the sequence of the first six letters from the top left.
Other sets of keys common to almost all keyboards are entering and editing keys (e.g., Enter, Delete, Insert), modifier keys (e.g., Control, Shift), navigation keys (e.g., arrows for up, down, left, right) and lock keys (e.g., Caps Lock). Additional keys are very operating system specific (such as the Windows and Apple keys).
Most keyboards also include a set of function keys at the top (F1, F2, etc.). The function keys typically perform a very specific task within a particular software application. So, what they do may depend on what you are doing on your computer at the time.
Most keyboards for desktop computers also contain a separate numeric keypad to the right. Even though there are numeric keys already in a row near the top, having them all close together makes it faster to enter numeric data. On smaller keyboards, like those on most laptops, these numeric keypads are typically no longer present due to space constraints.
Above, you can see a typical keyboard layout. Keep in mind that there are many different variations on this layout, although most manufacturers follow this general pattern:
Monitor(Display)

A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial form. A monitor usually comprises the display device, circuitry, casing, and power supply. The display device in modern monitors is typically a thin film transistor liquid crystal display (TFT-LCD) with LED backlighting having replaced cold-cathode fluorescent lamp (CCFL) backlighting. Older monitors used a cathode ray tube (CRT). Monitors are connected to the computer via VGA, Digital Visual Interface (DVI), HDMI, DisplayPort, Thunderbolt, low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) or other proprietary connectors and signals.
Originally, computer monitors were used for data processing while television sets were used for entertainment. From the 1980s onwards, computers (and their monitors) have been used for both data processing and entertainment, while televisions have implemented some computer functionality. The common aspect ratio of televisions, and computer monitors, has changed from 4:3 to 16:10, to 16:9.
Modern computer monitors are easily interchangeable with conventional television sets. However, as computer monitors do not necessarily include integrated speakers, it may not be possible to use a computer monitor without external components.